CVD vs HPHT Lab Diamond Growth Methods: What Singapore Buyers Should Know
Lab grown diamonds have become a major part of the engagement ring landscape in Singapore, but few buyers truly understand the differences between the two growth methods: **CVD (Chemical Vapour Deposition)** and **HPHT (High Pressure High Temperature)**. At Diamond Ateliers, where we create 80–100 bespoke rings monthly using carefully selected lab diamonds, we guide clients through these distinctions every day—because how a diamond is grown directly influences its quality, colour stability, and long-term value.
This guide breaks down CVD vs HPHT in clear, practical terms, using real-world experience from our founder-led studio. Whether you’re exploring lab grown diamonds in Singapore or comparing stones for your bespoke ring, understanding growth methods helps you choose better—and avoid common pitfalls.

H2: How HPHT Diamonds Are Grown H3: The HPHT Process in Simple Terms
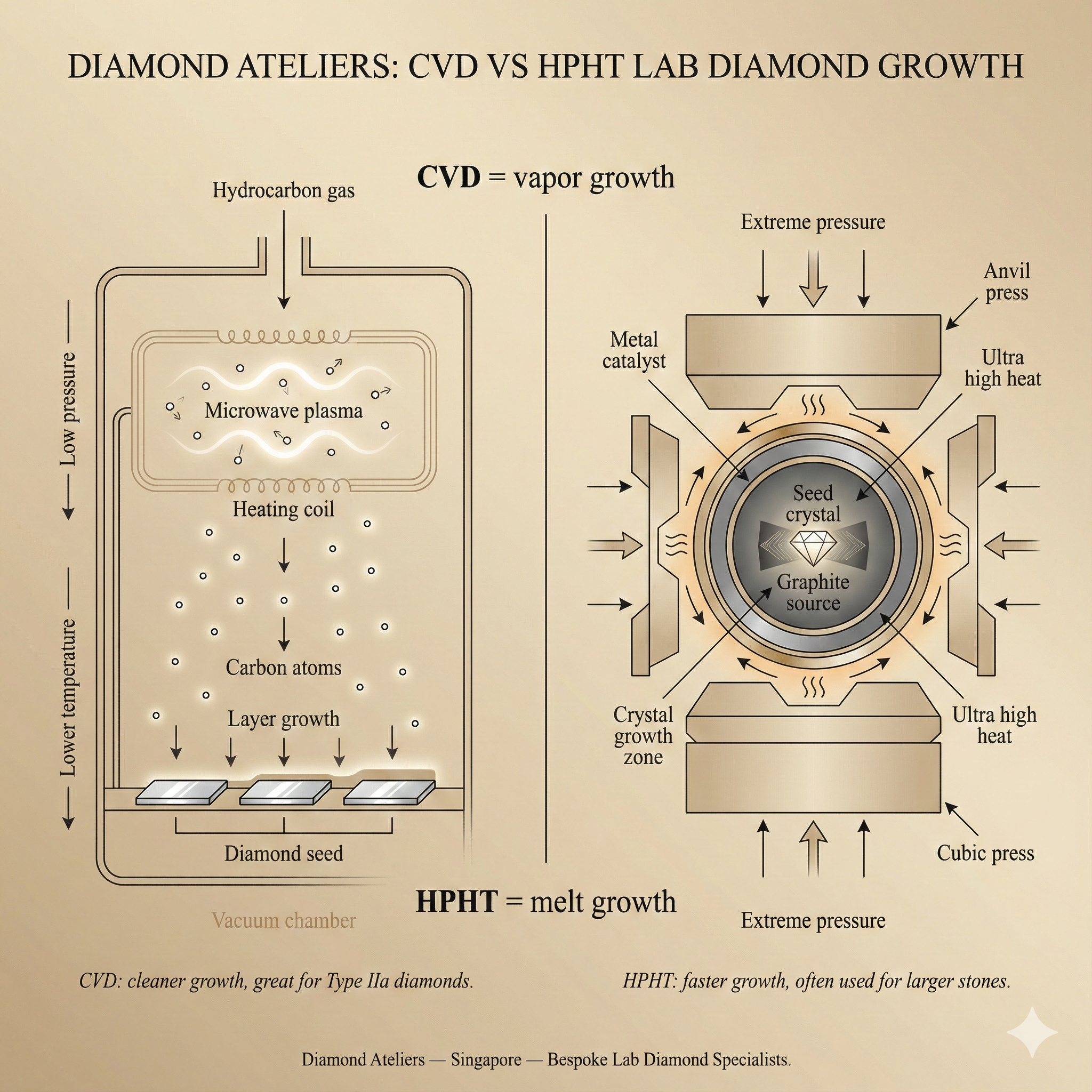
HPHT recreates the natural conditions deep within the earth—high pressure and high temperature—to grow diamonds from a carbon seed. This method produces fast growth and is often used for smaller diamonds or for colour-treated stones.
H3: Typical Characteristics of HPHT Diamonds
- Metallic Inclusions: HPHT uses metallic catalysts, which often results in magnetic or metallic pinpoint inclusions.
- Blue Undertones: Many HPHT stones exhibit a slight blue nuance due to boron presence.
- Colour Enhancement Common: Some HPHT diamonds undergo post-growth treatment to correct colour tints.
While well-grown HPHT diamonds can be beautiful, consistency across suppliers varies significantly. This is why our consultants always rely on detailed certification and in-house inspection before shortlisting any HPHT-grown diamonds for clients.
H2: How CVD Diamonds Are Grown H3: The CVD Growth Environment
CVD uses carbon-rich gas and controlled plasma to grow diamonds layer by layer. The process gives engineers tighter control over purity and strain levels, making CVD the preferred method for higher-end, Type IIa lab grown diamonds.
H3: Typical Characteristics of CVD Diamonds
- Cleaner Inclusions: CVD diamonds often contain fewer metallic inclusions.
- Consistent Colour: Colour is typically more stable and predictable without the need for post-growth treatments.
- Higher Chance of Type IIa: These diamonds have superior optical purity and are often chosen for premium bespoke pieces.
Most of the diamonds we recommend at Diamond Ateliers are CVD-grown, as they align with our standards for clarity, structural stability, and long-term brilliance.
H2: CVD vs HPHT — A Direct Comparison
| Factor | CVD | HPHT |
|---|---|---|
| Colour Stability | Excellent, minimal tinting | Can show blue tint; often treated |
| Inclusions | Non-metallic, cleaner | Metallic, may be magnetic |
| Typical Purity | Often Type IIa | Varies, often Type Ib |
| Growth Speed | Slower, controlled | Faster |
| Best Use Cases | Fine jewellery, solitaires | Smaller stones, coloured diamonds |
H2: Pricing in Singapore: What to Expect
In Singapore, CVD and HPHT diamonds are usually priced similarly for equivalent grades, though top-quality CVD Type IIa stones may command a slight premium due to demand. As a founder-led studio, we compare stones daily across global manufacturers, allowing us to shortlist only strong-value options for clients—especially those shopping for lab grown diamonds in Singapore for bespoke engagement rings.
For transparency, every diamond we present comes with full diamond certification from reputable labs such as IGI or GIA, along with our internal assessment of optical performance.
H2: Real Examples from Diamond Ateliers Example 1: 1.50ct CVD Type IIa, D Colour
A client wanted a crisp, high-clarity diamond for a modern six-prong ring. We shortlisted three CVD-grown stones with zero metallic inclusions and excellent light return. The final selection tested as Type IIa and became one of our most visually striking solitaires.
Example 2: 2.00ct HPHT, G Colour
Another client preferred a warmer tone. We identified an HPHT diamond with superb symmetry and minimal metallic inclusions. After confirming stability through certification, the stone was custom-set in a tapered cathedral setting to maximise its face-up size.
H2: How to Choose Between CVD and HPHT
Here’s the simple rule we share during consultations:
- Choose CVD if you want the most consistent colour, purity, and long-term stability for a solitaire engagement ring.
- Choose HPHT if you’re open to slight undertones or building a design with smaller side stones.
- Always prioritise certification to verify growth method, treatments, and structural data.
Our full Diamond Guide explains the 4Cs, fluorescence, and real-world buying strategies with examples from our studio.
H2: Book a Consultation at Diamond Ateliers
Choosing a diamond—whether CVD or HPHT—becomes far easier when you can inspect options side-by-side with transparent guidance. At Diamond Ateliers, all consultations are founder-led or conducted by our trained in-house team. We use 3D design, local craftsmanship, and real-time diamond sourcing to build rings that suit your budget and your vision.
Book your appointment to compare the best CVD and HPHT lab grown diamonds in Singapore.